In a world where attention is constantly pulled in different directions, concentration has become a real challenge. Notifications, deadlines, and mental noise make it hard to stay focused for long periods. This is why meditation techniques for concentration and focus are gaining strong attention in 2025 and 2026.
Meditation is no longer seen as a passive habit. It is now viewed as a practical mental training tool that helps sharpen attention, reduce overthinking, and improve productivity. Public discussions and personal experiences show that regular practice leads to measurable improvements in focus, clarity, and mental control.
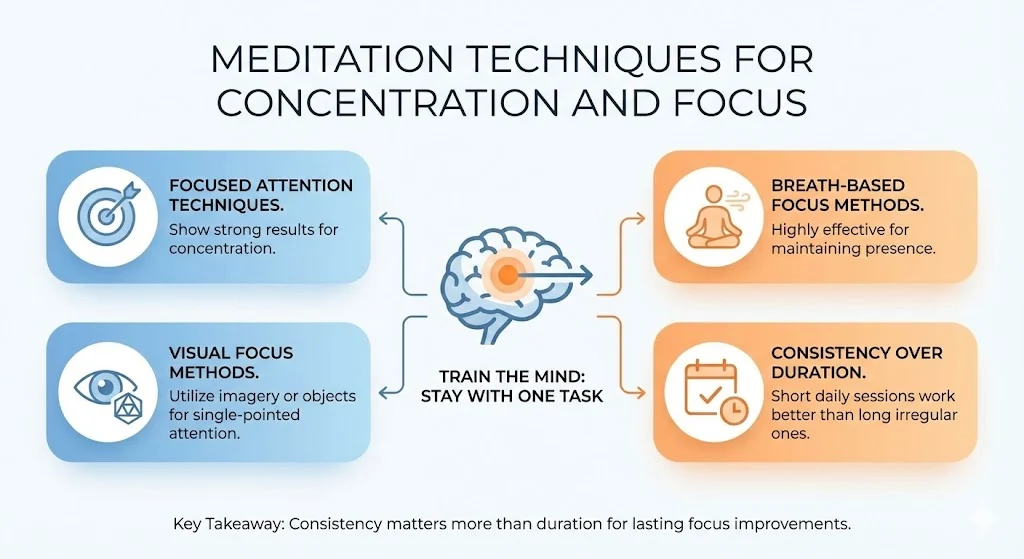
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
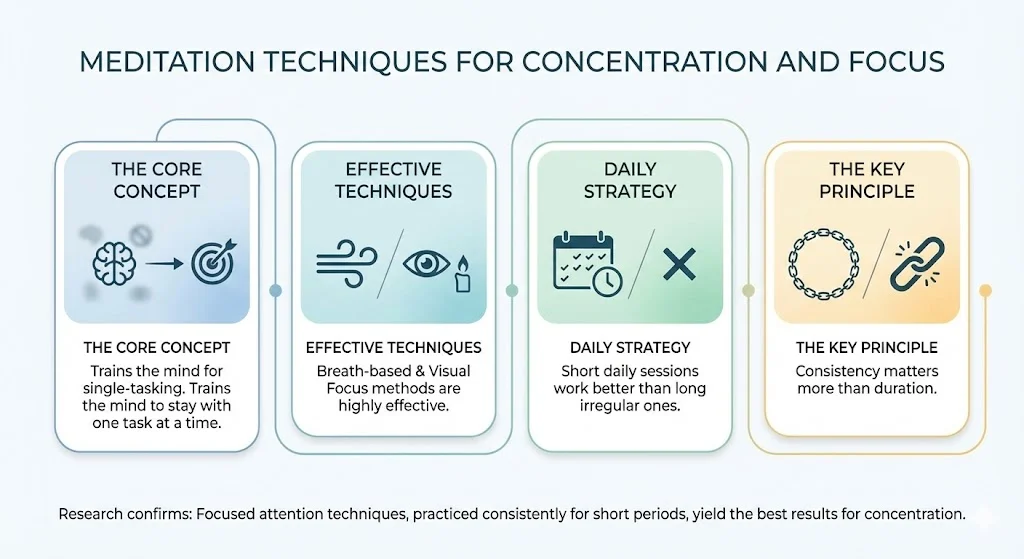
- Meditation trains the mind to stay with one task at a time
- Focused attention techniques show strong results for concentration
- Short daily sessions work better than long irregular ones
- Breath based and visual focus methods are highly effective
- Consistency matters more than duration
What Are Meditation Techniques For Concentration & Focus
Meditation techniques for concentration focus on training attention on a single object, sensation, or point of awareness. Instead of trying to stop thoughts, the practice teaches the mind to notice distractions and return to focus.
This process strengthens mental discipline over time. With regular practice, the brain becomes better at ignoring irrelevant thoughts and staying present. Studies on long term meditators confirm improvements in executive attention, reaction speed, and sustained focus.
Seven meditation techniques that improve concentration & focus

- Focused Attention Meditation: Attention is placed on one object like breath, sound, or a point between the eyebrows. Each distraction is noticed and attention is calmly brought back.
- Breath Counting Meditation: Each inhale and exhale is counted in sequence. When the count breaks, it restarts. This builds strong attention control.
- Mindfulness Meditation: Awareness stays with the present moment. Thoughts arise and pass without engagement. Focus improves through observation.
- Trataka Flame Gazing: Eyes rest on a candle flame without blinking. Visual focus deepens and mental distractions reduce.
- Body Scan With Breath Awareness: Attention moves through the body while staying connected to breathing. This grounds the mind and improves focus.
- Do Nothing Meditation: The body stays still and the mind is left untouched. Awareness remains without reaction, building mental stability.
- Guided Focus Meditation: A voice guides attention to breath or sensation. This helps beginners maintain focus without drifting.
These techniques work best when practiced daily, even for short durations.
Why Meditation Improves Focus And Attention
The human brain is not designed to multitask. Constant task switching weakens attention span and increases mental fatigue. Meditation reverses this pattern by slowing the mind and strengthening awareness.
Recent surveys show that around 89 percent of practitioners use breath centered techniques. These methods help stabilize attention and reduce mental wandering. Over time, meditation creates lasting changes in brain areas linked to focus and cognitive control.
Focused Attention Meditation
Focused Attention Meditation is one of the most effective techniques for improving concentration. The practice involves choosing a single point of focus and gently returning attention whenever the mind drifts.
Common focus objects include the breath, a mantra, a sound, or a visual point. Many practitioners also use third eye awareness between the eyebrows. With daily practice, the mind becomes more stable and distractions lose their grip.
This technique is widely admired because it feels active and empowering. People describe it as mental strength training rather than relaxation.
Breath Counting Meditation
Breath counting meditation adds structure to mindfulness practice. The meditator counts each inhale and exhale cycle in a simple sequence.
For example, inhale and exhale is counted as one. The count continues upward with each breath. When attention drifts, the count resets. This dynamic task exposes mental distraction quickly and trains focus through repetition.
Many people notice that staying present for even a few breaths can be challenging at first. Over time, the ability to stay focused improves naturally.
Trataka Flame Gazing Meditation
Trataka, also known as flame gazing meditation, has gained strong popularity in recent years. The practice involves gazing steadily at a candle flame without blinking.
As attention deepens, peripheral awareness fades and focus becomes sharp. Practitioners report strong improvements in concentration and mental clarity. Some describe entering calm alpha or theta brainwave states.
This technique appeals to people who prefer visual focus rather than breath based methods. It is often described as intense but highly effective.
Micro Meditation And One Minute Focus Practices
Modern lifestyles leave little room for long sessions. Micro meditation solves this problem by offering short focus resets throughout the day.
Sessions last between one and five minutes. Techniques include slow rhythmic breathing, brief breath counting, or simple awareness of posture and sensation. These short practices help reset attention during work breaks.
Many users report that even one minute of focused breathing reduces mental clutter and restores clarity.
Body Scan With Breath Awareness
Body scan meditation combined with breath awareness creates grounding and focus at the same time. Attention moves slowly through the body while staying connected to breathing.
This technique reduces restlessness and anchors awareness in physical sensation. It is especially useful for people who struggle with racing thoughts.
Practitioners report better emotional regulation and improved ability to stay present during demanding tasks.
Do Nothing Meditation For Mental Control
Do nothing meditation involves sitting still without trying to control thoughts, breathing, or posture. The goal is to remain aware without reacting.
This practice builds tolerance for mental discomfort and boredom. Over time, it strengthens the ability to observe thoughts without being pulled into them.
Many people report improved calmness during stressful conversations and better awareness of mental loops.
Guided Meditation For Focus
Guided meditation provides structure through verbal instruction. It is helpful for beginners who find silence challenging.
The guide directs attention to breath, body sensations, or visual focus. While guidance can feel relaxing, the real training lies in staying alert and present.
Many focus specific sessions last between five and ten minutes and are designed to improve attention without overwhelming the mind.
How Long Should You Meditate For Better Concentration
Consistency matters more than session length. Research and public feedback suggest that ten to twenty minutes per day delivers strong results.
Morning sessions are often preferred due to fewer distractions. Short daily practice leads to measurable improvements in sustained attention and reduced mind wandering.
Long term practitioners show lasting improvements across multiple attention systems.
Common Challenges And How To Handle Them
Difficulty concentrating is normal at the beginning. Mind wandering is not a failure but part of the training process.
Physical discomfort can be adjusted by changing posture or using a chair. Impatience fades with regular practice.
External noise becomes less disturbing as attention strengthens. Doubt usually disappears once subtle benefits become noticeable.
What People Are Sharing About Focus Meditation ( Data Taken From X )
Public opinion around meditation for concentration is highly positive. Many describe it as a mental gym that builds real resilience against distraction.
Users report better productivity, improved emotional control, and faster recovery from stress. Some mention reduced reliance on caffeine or stimulants.
Below is a summary of commonly shared experiences.
| Experience Reported | Common Outcome |
|---|---|
| Daily short sessions | Better sustained focus |
| Flame gazing practice | Sharper concentration |
| Breath counting | Reduced mind wandering |
| Silent sitting | Emotional stability |
| Micro meditation | Quick mental reset |
Scientific Support For Meditation And Focus
Studies on long term meditators show changes in brain regions responsible for attention and control. Improvements are seen in executive attention, selective attention, and response inhibition.
Reaction times improve and distractions lose impact. Neuroplastic changes confirm that attention skills can be trained with regular meditation.
This scientific backing has helped meditation move into high performance wellness spaces.
Making Meditation Part Of Daily Life
Meditation works best when integrated into routine. Fixed timing helps build habit strength.
Simple practices during daily activities also improve concentration. Eating, walking, or working with full awareness trains one pointed attention.
The key is regular exposure rather than perfection.
Conclusion On Meditation Techniques
Meditation techniques for concentration and focus offer a reliable way to sharpen attention in a distracted world. From focused attention meditation to flame gazing and micro practices, each method trains the mind to stay present.
Public experience and scientific evidence both confirm that daily practice leads to lasting mental improvements. With consistency and patience, meditation becomes a practical tool for clarity, productivity, and calm focus.







